Grommet edging plays an important role in ensuring the safety and longevity of cables and wires. This article delves into what grommet edging is, the common materials used for manufacturing it, and key considerations for selecting the right grommet edging to protect cables effectively.
What Is Grommet Edging?
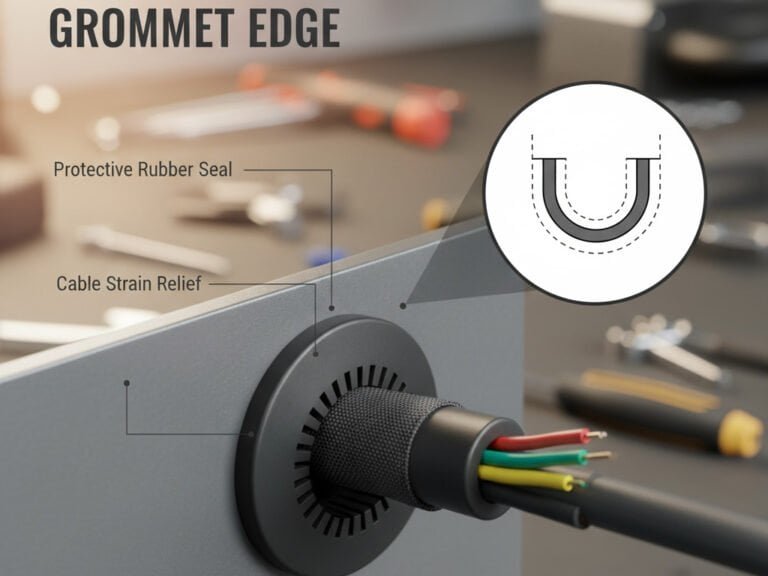
Grommet edging is a protective strip placed around cutouts or holes in panels to prevent cables from rubbing against sharp edges. Its structure directly affects performance: thicker and more rigid edging resists sharp surfaces better, while softer and smoother designs cushion delicate wires. Features such as reinforced lips or ribs help keep the edging firmly in place, ensuring reliable protection even in high-vibration environments.
Importance of Cable Protection
A single chafed wire can halt a production line, corrupt data, or ignite electrical hazards. Grommet edging serves as a protective barrier, shielding cables from the abrasive edges of metal or plastic panels. Without this safeguard, wires face risks of wear, vibration-induced damage, or exposure to harsh environmental conditions, potentially leading to costly downtime or safety violations. Beyond protection, grommet edging improves aesthetics by providing a clean, professional finish to panel cutouts.
Common Grommet Edging Materials
The effectiveness of grommet edging depends on selecting the right material, as different materials offer properties suited to specific environments and applications. In most cases, the edging is made from the same material as the grommet, which largely determines its performance.

Silicone
Silicone grommet edging is highly regarded for its excellent flexibility, thermal stability, and resistance to chemicals and UV light. It operates reliably across a wide temperature range and is commonly used in outdoor, high-temperature, or food-grade applications. The low coefficient of friction of silicone effectively reduces cable wear, while its outstanding elasticity ensures a snug fit even in irregular holes. Typically, silicone grommet edging is self-fastening with an embedded metal core, requiring no adhesives and offering a long service life.
EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer)
Known for extraordinary weathering, ozone, and UV resistance, EPDM grommet edging is favored for rugged outdoor and automotive uses. It is chemically stable and durable, though it has limited compatibility with hydrocarbons and halogenated solvents. EPDM comes in self-fastening versions with steel reinforcement, facilitating quick grommet installation without adhesives.
PA(Nylon)
Nylon grommet edging is often molded from nylon 6/6. Its strong points are toughness, abrasion resistance, and good dimensional stability. Nylon also exhibits resistance to chemicals and UV radiation, making it suitable for many indoor applications. Nylon grommets usually require adhesives for installation, which increases labor and cost and may lead to bond failure in moist or high-stress environments.
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)
PVC grommet edging is a cost-effective, versatile option with good chemical and abrasion resistance. While rigid in nature, it is made flexible via plasticizers and often includes an aluminum or steel core for structural support. PVC is flame-retardant. It is suitable for indoor industrial applications and office furniture.
PE (Polyethylene)
Polyethylene grommet edging is lightweight and economical, with excellent electrical insulation and abrasion resistance. Its limitations include lower heat tolerance, poor UV stability, and a lack of flame retardancy. PE grommets often require adhesives and may have installation challenges on rough edges.
Encapsulated Metal Spring Fastening Grommets
These designs combine a spring steel core with a durable polymer coating, typically a thermoplastic elastomer (TPE). This combination provides exceptional edge retention without adhesives, significantly reducing installation time and costs. They offer excellent abrasion resistance, chemical stability, flame, and vibration. They are ideal for aerospace, automotive, telecommunications, and industrial automation.
Key Factors in Choosing Grommet Edging
Choosing the right grommet edging involves balancing several factors to match the solution to your application’s needs. Below are the key considerations:
Usage Environment
Consider the ambient temperature range, exposure to chemicals, UV light, moisture, vibration levels, and safety standards. For outdoor or harsh environments, materials like silicone rubber, EPDM, or encapsulated metal edging perform best. For indoor or cost-sensitive applications, nylon or PVC may be sufficient.
Dimensions
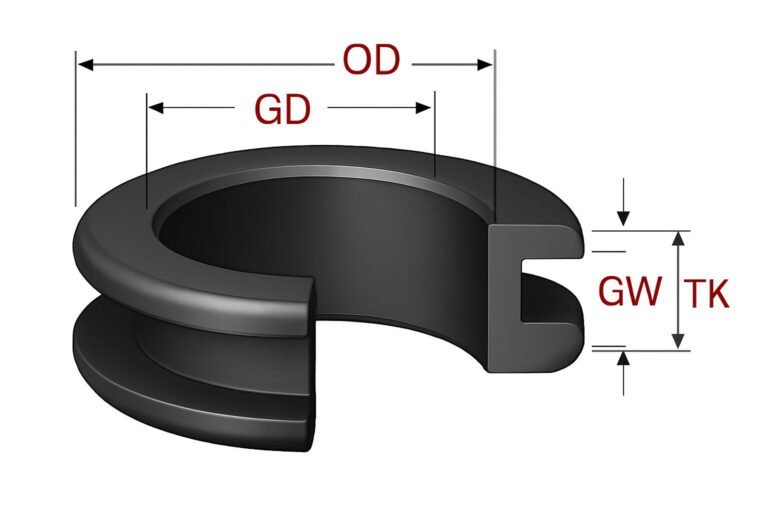
Grommet edging must match the panel thickness and hole geometry, whether round, oval, or custom. It is essential to measure the sheet or panel thickness and the cable bundle diameter to select the right grommet size, avoiding loose fits that compromise protection or excessively tight fits that complicate installation.
Installation Method
Traditional grommet edging, such as nylon or rubber grommet edging, often requires adhesives, tape, or clamps, increasing labor and material costs. Snap-on systems streamline installation by eliminating adhesives, making them ideal for high-volume production or time-sensitive projects.
Cost and Maintenance
Polyethylene grommet edging is budget-friendly but may require more frequent replacement in demanding environments. In contrast, encapsulated metal or silicone options, while pricier upfront, offer extended lifespans and minimal maintenance.
Conclusion
Grommet edging is a vital solution for safeguarding cables and ensuring operational reliability across industries. Welcome to contact Flexiparts to get various materials and sizes of grommet edging solutions.