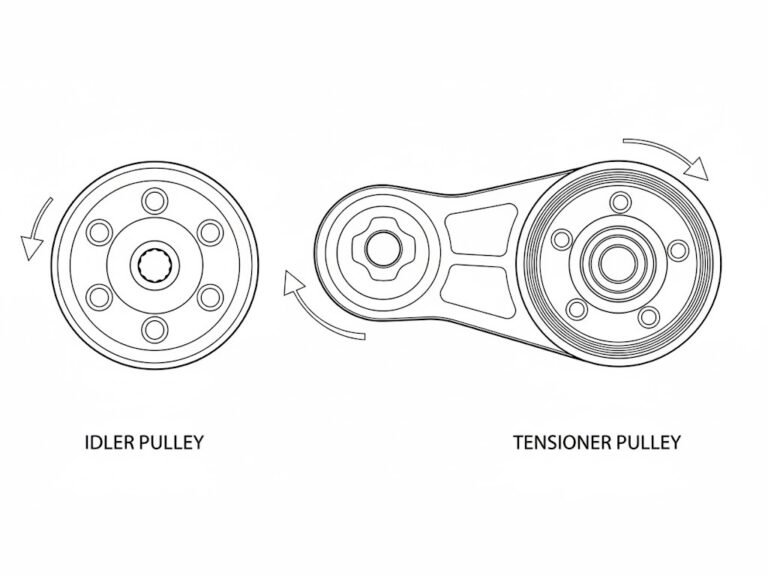
In modern engine systems, belt-driven components transfer power between different parts. To ensure the belts are maintained at the correct tension and move properly, idler pulleys and tensioner pulleys are used. Confusing the two during diagnosis or replacement can lead to repeated failures and expensive repairs.
What Is an Idler Pulley?
An idler pulley is a stationary component that guides a belt or chain along its intended path, increasing its contact with driven components. It is mounted on a fixed bracket with a sealed bearing and rotates freely, without any spring or damping mechanism. Its main function is to redirect the belt path, improve belt contact, and prevent slipping, ensuring smooth operation of the system. Common signs of wear include bearing damage, misalignment, unusual noises that vary with engine speed, or grease leakage. learn more about the idler pulley
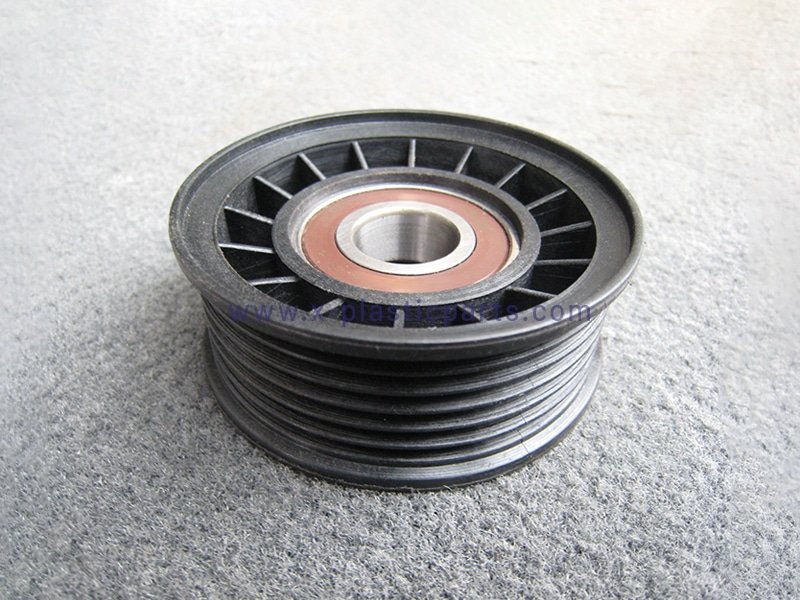

What Is a Tensioner Pulley?
A tensioner pulley is mounted on a spring- or hydraulically-loaded pivot arm as part of the belt tensioner assembly. It maintains proper belt tension automatically, compensating for belt stretch, temperature changes, and variations in accessory load. Many modern tensioners also incorporate damping features to reduce vibration and belt flutter. Depending on the design, the pulley may be replaced individually, but in many cases, the entire tensioner assembly must be replaced when worn.
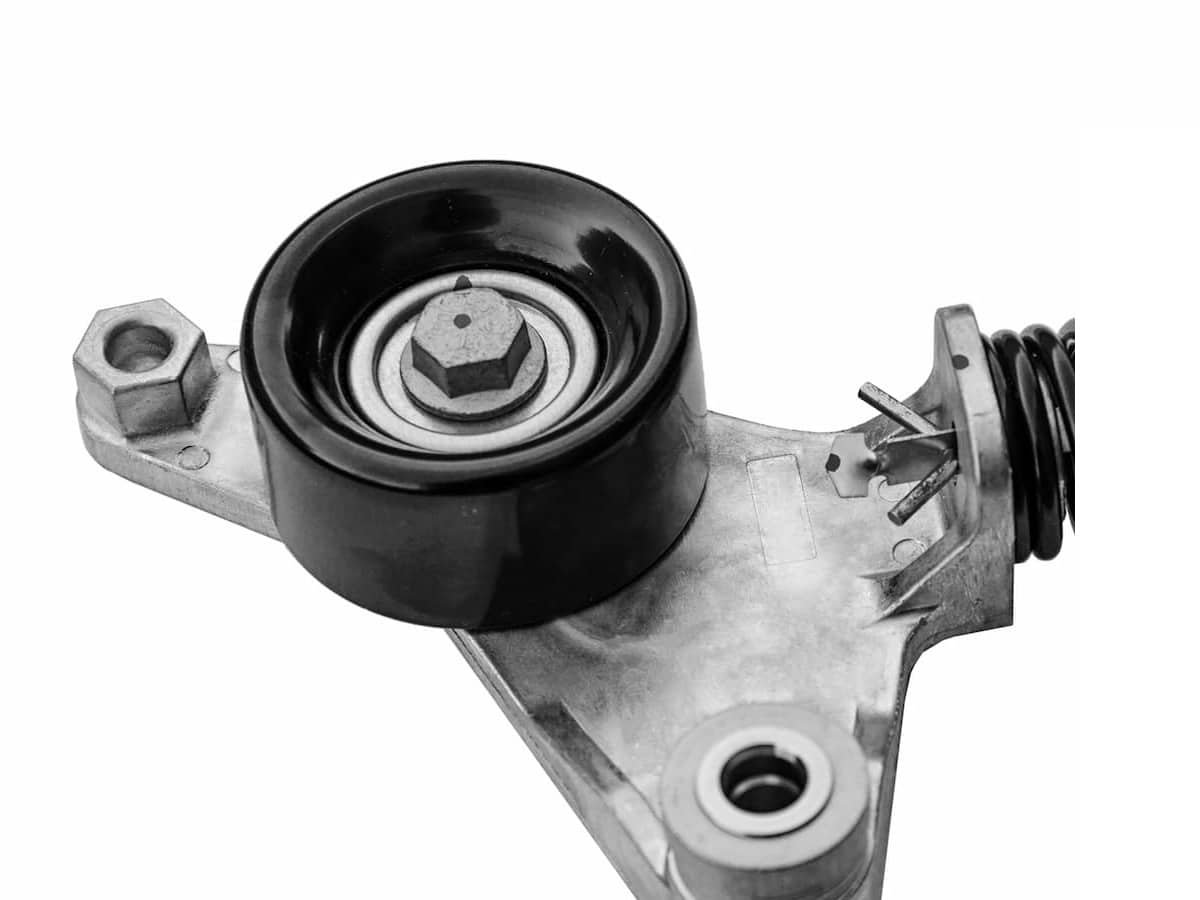

Customized Idler Pulley vs. vsTensioner Pulley: Key Differences
While both idler and tensioner pulleys serve essential roles in a belt system, they differ in function and design. Let’s take a closer look at the key differences between the idler pulley and the tensioner pulley:
Functionality
- Idler pulleys are passive components. They guide and support the belt but do not affect its tension.
- Tensioner pulleys, on the other hand, are dynamic components. They adjust the tension on the belt by using a spring or hydraulic system, ensuring that the belt stays tight and functions properly.
Design
- Custom idler pulleys are generally simpler in design. They consist of a wheel that rotates freely, typically without any tensioning mechanism.
- Tensioner pulleys are designed with built-in tensioning mechanisms such as springs or dampers. These components allow the pulley to adjust itself as needed, ensuring that the belt tension remains consistent.
Purpose
- The primary role of an idler pulley is to redirect the belt and keep it in alignment. It does not actively adjust belt tension.
- The tensioner pulley ensures that the belt is neither too tight nor too loose. It automatically compensates for belt stretch and changes in the system’s load to maintain proper tension.
Wear and Maintenance
- Idler pulleys are more prone to wear due to friction and prolonged use, but typically require less frequent maintenance compared to tensioner pulleys.
- Tensioner pulleys require regular inspection because their spring or hydraulic mechanism can degrade over time. If a tensioner pulley fails, it can lead to incorrect tension, potentially causing severe damage to other components in the system.
Symptoms of Failure
- A failing idler pulley may cause noise or improper belt alignment, which can lead to belt wear or misalignment.
- A failing tensioner pulley is often more noticeable, as it can cause the belt to slip, squeal, or even break. Improper tension can result in engine misfires, decreased performance, or excessive wear on other engine components.
Conclusion
If you’re looking for high-quality, customized pulley solutions, Flexiparts is a trusted manufacturer offering expert advice and precision-made pulleys for all your needs. Whether you need an idler pulley or a tensioner pulley, Flexiparts can provide you with the ideal solution for your system’s requirements.