Rapid injection molding service is transforming manufacturing by enabling faster production, lower costs, and high flexibility for prototypes and low-volume parts. Techniques like fast or quick injection molding let businesses quickly realize designs, iterate on products, and deliver functional parts efficiently. From automotive to medical sectors, rapid tooling injection molding is reshaping production approaches. This article examines its benefits, challenges, technological advances, and comparison with traditional molding methods.
What Is Rapid Injection Molding?
Rapid injection molding is a fast, efficient method for producing plastic parts by creating molds from 3D designs and injecting molten material to form precise shapes. Its speed in mold design and production makes it ideal for prototyping, product testing, and short-run manufacturing.
Benefits of Rapid Injection Molding
1. Fast Turnaround
Molds can be produced in days, enabling a quick transition from design to functional parts. Short cycle times also speed up production.
2. Cost-Effective for Low Volumes
Uses lower-cost, flexible tooling—ideal for prototypes and small batches, offering a more affordable option than traditional steel molds.
3. Easy Design Iteration
Perfect for prototyping. Parts can be produced, tested, and adjusted quickly, allowing fast refinement before mass production.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Part Size and Complexity Limits
Best for small to mid-sized parts. Softer tooling materials may not support very large or highly complex designs.
2. Tooling and Material Constraints
Rapid tooling can wear faster, and choosing the right plastic is critical to avoid defects like warping or poor flow.
3. Timeline and Cost Balance
Complex designs may need multiple iterations, increasing time and cost. Managing speed, quality, and budget is essential.
How Rapid Injection Molding Works?
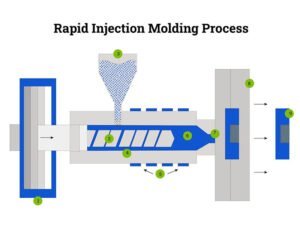
Rapid Injection Molding Process
- DFM Review & Quotation: Evaluate part geometry, material needs, and manufacturability to provide an accurate quote and lead time.
- Rapid Mold Design & Fabrication (Aluminum / Soft Metal / 3D-Printed Tooling): Create and build a fast-turnaround mold optimized for prototyping and low-volume production.
- Material Preparation & Injection Molding: Melt and inject the selected material into the mold under controlled pressure and temperature.
- Cooling, Ejection & Inspection: Allow the part to cool, eject it from the mold, and perform dimensional and visual checks.
- Post-Processing (Deflashing, Polishing, Painting, Printing, etc.): Apply required finishing steps to meet appearance and functional requirements.
- Delivery of Low-Volume Parts: Ship fully inspected parts ready for testing, assembly, or market validation.
Materials Commonly Used in Rapid Injection Molding
Rapid injection molding mainly works with a small, easy-to-understand group of plastics. Here is the simplest breakdown to avoid confusion:
1. Standard Plastics (Used for Most Parts)
These cover around 80% of rapid molding needs.
- ABS – Strong, reliable, good surface finish.
- PC – High strength and heat resistance; can be clear.
- PP – Lightweight and chemical-resistant.
- Nylon (PA) – Tough and wear-resistant.
2. Flexible Materials
Used when softness or sealing performance is required.
- TPE/TPU
- Silicone
Ideal for grips, seals, and flexible components.
3. Higher-Performance Plastics
For parts that need more strength, rigidity, or heat resistance.
- PC-ABS
- Glass-filled Nylon
- POM
(Note: Ultra-high-performance materials like PEEK or Ultem are possible but not typical for rapid molding timelines.)
Applications of Rapid Injection Molding
Prototyping and Testing for Product Designs
Rapid injection molding is ideal for creating functional prototypes quickly. Rapid injection molding delivers parts that closely resemble the final product in both design and material properties. This speed allows businesses to test designs, identify flaws, and make adjustments before full-scale production, reducing costly delays and improving product quality.
Low-Volume Production and Small Batch Runs
For low-volume production, rapid injection molding offers a cost-effective alternative to traditional methods. Creating expensive, high-volume molds for small runs isn’t economical. Rapid molding allows for the production of smaller batches, reducing costs while maintaining high-quality standards. This is especially beneficial for niche markets, limited releases, or specialized parts where mass production isn’t feasible.
Industries Benefiting from Rapid Injection Molding
- Automotive Industry
- Medical Devices
- Electronics
- Consumer Goods and Packaging
- Aerospace
Rapid Injection Molding vs. Traditional Injection Molding
Comparing Speed and Efficiency: What Makes Rapid Molding Faster?
Rapid injection molding is faster due to quicker tooling and shorter lead times. Traditional molds take weeks to create, while rapid molds can be made in just days using softer metals or 3D printing. This faster mold production, along with shorter cycle times during molding, allows rapid injection molding to deliver parts more quickly, making it ideal for time-sensitive projects.
Cost Considerations: How Rapid Injection Molding Saves Money?
Rapid injection molding is more cost-effective for small runs or prototypes. Traditional molding requires expensive molds that take longer to produce, which increases costs. In contrast, rapid molding uses low-cost tooling and faster production, reducing both initial investment and operational costs, making it a better option for low-volume or test production.
Tooling Differences: Comparing Rapid and Traditional Molds
The main difference lies in the tooling material. Traditional molds are made from hard steel or aluminum, built for durability and mass production, but are costly and take longer to produce. Rapid molds use softer metals or 3D printing, which are quicker and cheaper to make but are not as durable, making them ideal for smaller runs or prototyping.
Limitations of Traditional Molding Versus Advantages of Rapid Molding
While traditional injection molding is perfect for large-scale production, it’s costly and time-consuming for low-volume or custom projects. Rapid injection molding, however, offers lower tooling costs and faster lead times, making it a flexible, cost-effective option for small batches, prototypes, and quick design iterations.
Here’s a table comparing Rapid Injection Molding and Traditional Injection Molding:
| Aspect | Rapid Injection Molding | Traditional Injection Molding |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Faster mold creation and shorter cycle times | Longer mold creation and cycle times |
| Cost | Lower initial cost and production costs | High upfront tooling and production costs |
| Tooling | Uses softer metals or 3D printing for molds | Uses hard steel or aluminum for durable molds |
| Production Volume | Ideal for low-volume and prototype runs | Best for high-volume, mass production |
| Lead Time | Quick turnaround, molds created in days | Longer lead time due to mold fabrication |
| Flexibility | Suitable for quick design changes and iterations | Less flexible for design changes during production |
| Durability of Molds | Molds are less durable, suitable for short runs | Molds are highly durable, designed for long-term use |
| Applications | Prototyping, low-volume, small batch production | Large-scale manufacturing, mass production |
When to Choose Rapid Injection Molding?
When deciding whether to use rapid injection molding, several factors need to be considered:
- Volume: Rapid injection molding is best for low to medium-volume production. For large-volume production, traditional injection molding may be more cost-effective as the initial tooling costs are spread over a larger number of parts.
- Part Complexity: If the part has a complex design or intricate features, rapid molding can still deliver the required precision. However, if the part design is simple and can be easily mass-produced, traditional molding may be a more economical choice in the long run.
- Lead Times: If you need a product fast, rapid injection molding is the clear choice. With faster mold creation and shorter production cycles, it can dramatically reduce lead times compared to traditional molding, which requires more time for tooling and setup.
- Budget: Rapid injection molding has lower upfront costs compared to traditional methods, making it a more budget-friendly option for projects with tight financial constraints. If you’re working with a limited budget or need to test multiple iterations, rapid molding provides cost-effective flexibility.
Technological Advancements Enabling Rapid Injection Molding
3D Printing for Mold Creation
3D printing allows fast mold production from digital designs, cutting both time and costs for prototypes and low-volume runs. It offers flexibility for quick design iterations with materials like resins or metals.
CNC Machining for Precision Tooling
CNC machining enables precise mold creation with minimal lead time. It ensures accuracy, making it ideal for complex parts and low-volume production.

Advanced Materials for Rapid Molds
New materials, such as aluminum alloys and soft metals, reduce tooling time and cost. They’re durable enough for low-volume production, making rapid molding more affordable.
Simulation and Virtual Prototyping
Simulation software lets manufacturers test part designs digitally, catching issues early and reducing the need for multiple physical prototypes, speeding up development.
Automation and Smart Manufacturing
Automation and smart manufacturing streamline the process, improving consistency and speed. Sensors track variables like pressure and temperature for real-time adjustments, ensuring precision.
Integration of Hybrid Manufacturing Techniques
Hybrid manufacturing combines 3D printing and CNC machining, offering the speed of 3D printing and the durability of CNC for more efficient mold production.
These advancements have made rapid injection molding faster, more precise, and cost-effective for modern manufacturing needs.
Conclusion
Rapid injection molding company offers a compelling solution for quick prototyping, low-volume production, and cost-effective manufacturing. With its faster turnaround times, reduced tooling costs, and flexibility in design iteration, it stands out as a valuable method for industries requiring speed and precision. However, challenges such as part size limitations, material selection, and managing production costs must be carefully considered to fully leverage its benefits. By understanding the technology, evaluating the specific needs of a project, and making informed decisions on tooling and materials, businesses can harness the power of rapid injection molding to streamline their production processes and bring products to market faster than ever before.
FAQ About Rapid Injection Molding
When you need functional, production-grade plastic parts (not just appearance) with realistic material properties — for fit, strength, mechanical testing — and you want more consistent quality, better surface finish, and scalability beyond single prototypes.
No. Rapid injection molding is generally cost-effective for prototypes, functional testing, and low- to mid-volume production. Its faster, lower-cost tooling makes it much cheaper than traditional steel molds for small batches, while still delivering high-quality parts quickly.
Yes. With advanced tooling like 3D-printed or EDM molds, rapid injection molding can produce complex parts with fine features and tight tolerances, making it ideal for prototypes and small-batch production.




